Our brain is full of mysteries like a still unopened veil of secrecy. Years of work still cannot fully explain the brain. But some psychological effects give us clues about how our brain works. According to behavioral science, every person experiences some psychological effects from time to time, no matter how different our characters are.
The most common psychological effects are as follows:
1) Pratfall Effect

The Pratfall Effect shows us that perfection is not well received in human psychology. According to Pratfall, you are more likely to be liked and liked by other people as long as you have flaws.
2) Pygmalion Effect

The Pygmallion Effect, which is briefly summarized as high beliefs and expectations leading to high performance, is an effect found in the minds of most successful people.
You can click on the title for related content about this effect. 

3) The Election Paradox

The more alternatives you have on an issue, the less the determination on the alternative will be. As the brain analyzes each alternative, it is more difficult to reach a clear conclusion. That’s why you have a harder time making a decision when you have a lot of options.
4) Spotlight Effect

Contrary to popular belief, the mistakes you make are not noticed as much as you might expect. If you’ve made a mistake and you get the perception that people see it right away, you’re in the spotlight.
5) Focusing Effect
If you focus too much on one thing, you are more likely to miss out on opportunities around you. In short, it is a situation where your focus on a single detail prevents you from seeing the big picture.
6) Audience Effect

This effect, also called the Bystander Effect, is the situation where the more people around you when you ask for help, the less people want to help.
What you see on the news is, “There are so many people, how can anyone not help?” The phenomenon you interpret is called the Bystander Effect in the psychology literature.
7) Bandwagon Effect

No matter how much people adopt an event, situation, or ideology, according to the majority of them, it is the motivation to accept that thing. It can also be called a kind of sympathy for being on the side of the strong.
8) Underdog Effect
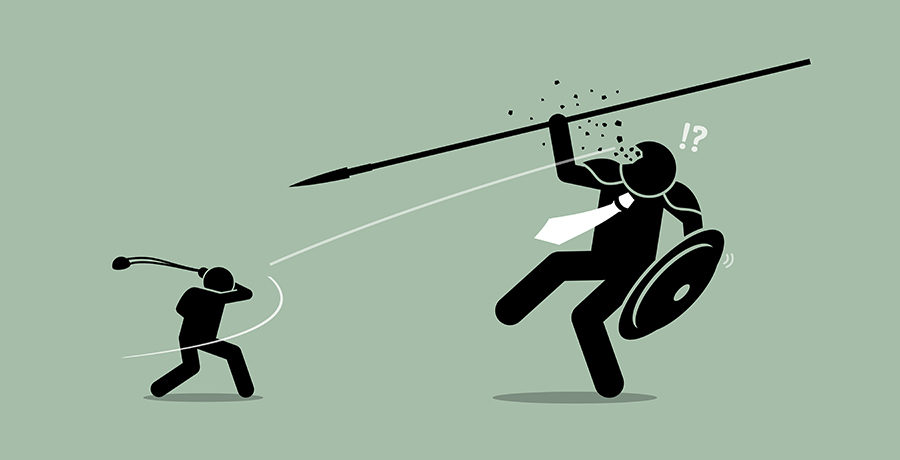

In contrast to the Bandwagon Effect, this time it is the urge to be on the side of the oppressed and the weaker, to support. For example, if you don’t take sides while watching a sporting event, you may want the weak to win from time to time. This situation is called the Underdog Effect.