The question of what is atomic physics explains the science that deals with the atom in its most general sense. Another feature of atomic physics, as the name suggests, is that it is among the sub-branches of physics. As with all sub-branches of physics, atomic physics is the branch of science that studies all levels of the atom. Structural relationships between different atoms are among the main areas of study of atomic physics. Likewise, atomic interactions, atomic and molecular structures are also included in the field of atomic physics. Wave functions, energy levels, electromagnetic percolation, atomic model and molecular spectrum explain these areas.
Almost everyone knows that atoms are the smallest building blocks of matter. However, there are important features to know about it. First of all, atoms are not very small building blocks of the sun. Quantum physics is needed for them to be studied. Much more refined atomic structures can be resolved based on relativity quantum physics. Because their structure and volume are so small, it is possible to explain atoms only indirectly. At this point, we come across spectroscopy. By means of spectroscopy, the radiations absorbed or emitted by the substances are measured.
Prerequisite for Understanding Atomic Physics: What is Atom?
At the most extreme of our knowledge today, atoms are known as the smallest building blocks. It would be correct to call this the smallest pieces of matter known in the universe that we know and are trying to assimilate. Another usage name of atom is eycik. The etymological origin of the word atom, like many other words, goes back to the Ancient Greek language. The word atom used today is derived from the word “atomos”. The first person to bring this usage to history is the famous Greek atomist Democritus. With the very early works of Democritus, information about the atom began to be obtained.
It is known today that it is impossible to see with the naked eye and can only be examined with an atomic microscope. Atoms have nuclei of their own. Each atomic nucleus has electrons surrounding it. These electrons charge the atomic nucleus negatively. The nucleus of the atom, on the other hand, consists of positively charged structures and also called uncharged neutrons. When the number of protons and electrons in the atomic nucleus is equal, the atom is uncharged. When the balance between electrons and protons cannot be established, an unstable structure emerges. The name of this structure is the ion.
How Did the Mysterious History of the Atom Develop?
In order to answer the question of what is atomic physics in the most correct way, it is necessary to know the history of the atom. Numerous scientific studies have been carried out about the atom since the ancient Greek thinker Democritus. Ancient Greece left a very rich accumulation of thinking about atoms and matter. Empedocles and Aristotle’s views on matter also advanced the study of atoms. The 4 states of matter, or more accurately 4 basic items, were put forward by these thinkers. The four main substances are fire, earth, air and water to these thinkers. During the following ages, no additions were made to atomic studies according to our current knowledge.
Until the work of John Dalton. Dalton was the first to introduce the modern concept and theory of the atom. Dalton was the first person to draw up a table of his own and that atoms were studyable. In the continuation of Dalton’s century, Mendeleev goes down in history as the person who created the periodic table for the first time. After him, JJ Thomson first described the electron, followed by Rutherford’s proton. Beyond all these, Bohr’s works have been the main direction of history.
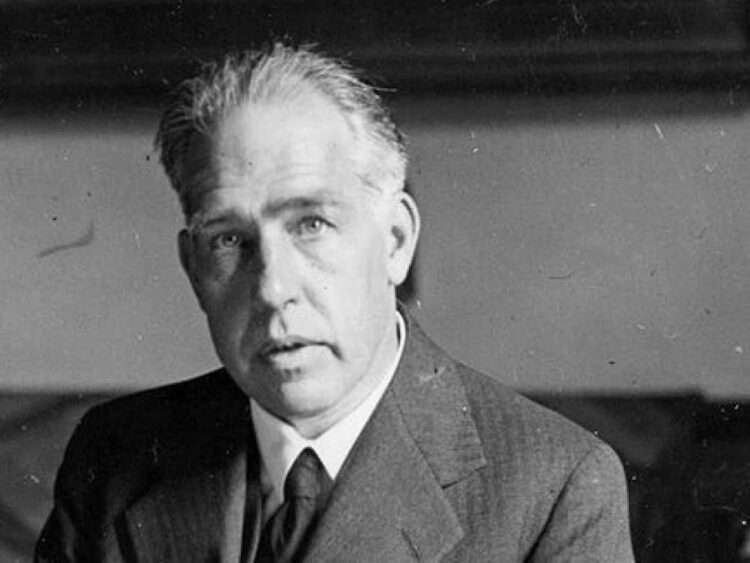
What Comes to Mind When You Say Atomic Physics: Niels Bohr
Niels Bohr is one of the first pioneers that comes to mind when it comes to atomic physics. This is because of Bohr’s incredible contribution to the world of science. He has carried out atomic studies in numerous fields, especially in quantum physics. There is also an atomic model, named after Bohr and known for the first time in history. Bohr developed this model by taking the work of his predecessor, Rutherford, forward. In this sense, we can say that atomic studies, like all scientific knowledge, progress cumulatively. The accepted thesis in atomic studies before the Bohr model was the idea that electrons move around the nucleus of the atom.
Bohr, on the other hand, tried to change this idea by presenting various assumptions and studied the motions of electrons. According to this model, electrons cease to be completely fixed structures. Bohr tries to explain this assumption with the “excited atom”. According to the model, electrons moving in circular motion at the point closest to the atomic nucleus are stationary. In other words, it is stable and does not scatter energy around it. However, it is argued that if enough energy is given to this electron, it will jump and become unstable.
A Critical Tool in Atomic Physics: Spectroscopy
We briefly mentioned spectroscopy in our previous sections. Spectroscopy has an important place in atomic physics in terms of the fields in which it is used. Spectroscopy, also known as spectroscopy, examines the motions of matter. Among these movements are the most fundamentally oscillating and absorbing particles. While doing this, vehicle light and sound are used. In the first place, it should be noted that spectroscopy is not used for purely chemical analysis. It is used for many fields and purposes other than chemical analysis. Physics, photonics, and optical purposes are among these, and these fields benefit from spectroscopy.
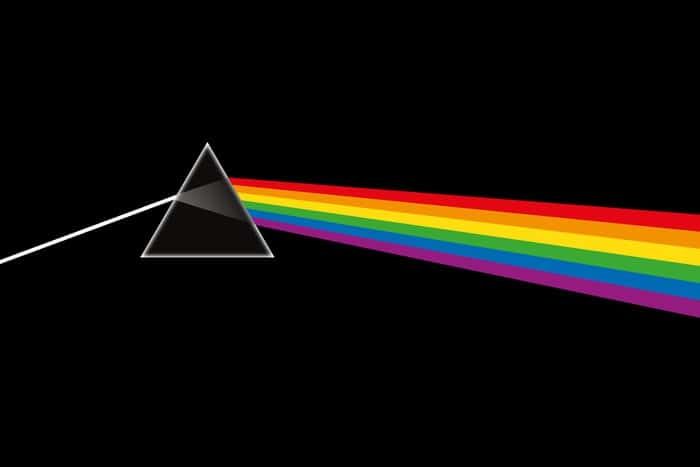
Any work in the sub-branches of these fields can benefit from this tool. Among these study areas, the interaction between light and matter can be given as an example. The emblem of Pink Floyd, which shook the music culture and added a unique interpretation, is also related to spectral science. The group emblem, which resembles light beams seeping through a triangular prism, is actually closely related to spectroscopy. The tool also serves to study the amount of radiation emitted by substances and their interactions.
What Fields Does Atomic Physics Examine?
We have compiled the most interesting part of our article titled What is atomic physics for you. Atomic physics, in its most general sense, is of great importance for physics and chemistry sciences. It progresses by doing research on the issues between these two disciplines. Atomic physics first begins by determining the properties of the atom. After that, it continues by making determinations about the structure of atoms and molecules. However, it aims to provide information about atomic radiations and transformations in atomic structure. Atomic physics also provides benefits in determining the energy levels of the atom.
It can determine some properties of photons, as well as make definitions about the processes of the photoelectric event. Considering all these features and fields of study, atomic physics has a very comprehensive study discipline. Thanks to these features, atomic physics is among the most popular fields of modern science and physics.
The most diverse and rich information about the atom, which is the premise of explaining matter, is obtained thanks to atomic physics. Finally, atomic physics also has many applications.
What are the Application Areas of Atomic Physics and What Are They?
The question of what is atomic physics undoubtedly brings with it the application areas of atomic physics. Before we move on, we must say that atomic physics has many applications in numerous fields. Nanotechnology is one of the application areas of atomic physics. Nanotechnology, which makes everyday life practical in the modern age, owes a lot to atomic physics.
Nanotechnology is used in many fields on its own. From this point of view, it can be seen that the relationship of atomic physics with nanotechnology opens up countless possibilities. Nanotechnology is used in the production of materials, especially in the defense and weapons industry. Nanotechnology is also used in electrical and computer technologies and aviation systems.
Nanotechnology is also used in the production of environmental policies or in the pharmaceutical industry. Considering all these areas, we can say that atomic physics is like a momentum that drags our age into the future. In addition, thanks to atomic physics, electron microscopy, laser technology and automatic door production are also carried out.
The greatest invention that atomic physics brought to the field of health is the electron microscope. Thanks to this microscope, living things that cannot be seen with the naked eye can be identified. Viruses, bacteria and microbes are among them.