Ever since humans began to exist, they have always been curious about the sky. He tried to make sense of these events that took place in the sky. The disappearance of tens of stars that appear at night, the disappearance of some stars in the same place in the sky, and the disappearance of some have made people wonder. Astronomy emerged thanks to this curiosity.
With this curiosity, the work of examining the sky, which started with small and simple observations, has become a branch of science with a great accumulation over time. We will tell you about this branch of science astronomy. We will answer your questions such as what is astronomy , what it studies, what is its history and what are its sub-branches. Here is our article on astronomy.
What is Astronomy?
It is a branch of science in which studies are carried out to explain and discover celestial bodies. The term astronomy is derived from the ancient Greek words astro and nomos, meaning the law of the stars.
In fact, human beings have put their daily, monthly and yearly affairs in order with the movements of the stars. This is how the interest in space began, and it became a branch of science over time, as these little observations combined. The curiosity of mankind towards celestial events, the formation of the world, briefly the universe, has led to the birth of the science of astronomy.
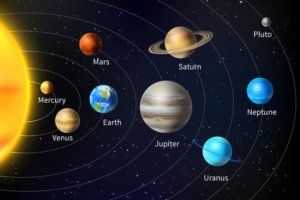
This field, also called astronomy: This is the branch of science that examines the movements of celestial bodies, their positions, measuring their distances from each other, their relations between them and their structures in terms of chemistry and physics. That is, it is the study and study of celestial bodies such as the Sun, Moon, stars, galaxies, meteorites, comets, and even clouds of dust and gas. It is a branch of science that studies the movements, properties, behaviors and chemical structures of celestial bodies.
History of Astronomy
Especially in the works to be done in agriculture, human beings had to know the history of the seasons and some periodic events in advance. So, in a way, they needed a calendar to know about these events. Seasonal changes were recorded in Egypt in the two millennium BC and papyri were found indicating that these changes were associated with the birth of the stars.
The founders of modern astronomy were the Sumerians, famous for their temples called the Ziggurat . They believed that the gods were here and sought their gods in the sky. And in this way, they observed and recorded the planets and stars visible to the naked eye. Babylonian astronomers in Mesopotamia put forward advanced mathematical methods to explain eclipses and planetary movements.
The Mathematical System That Puts the Earth at the Center of the Universe
Greek astronomers, on the other hand, based their movements in the sky with geometry. Thus, this branch of science has become a more systematic science that can explain celestial events. The last astronomer of Greek astronomy was Ptolemy. He established a mathematical and geometric system that puts the Earth at the center of the universe.
His views occupied a great place until the Copernican heli-centered system. Galileo Galilei is 17. He observed the Moon, Sunspots, Venus and the Milky Way for the first time with his own telescope in the 19th century. Galileo, who found Jupiter and its four moons, created an important turning point in the science of astronomy.
What Does Astronomy Study?
Mankind wanted to observe celestial bodies in order to understand the universe. These researches, which started with the naked eye, have turned into a big science today. Astronomy examines the movement of celestial bodies, from their chemical structures, to their physical properties, from past to present, to their evolutionary structures. Modern astronomy has the field of study of the behavior of all objects in space, their properties and their positions between each other.
sub-branches of astronomy
The science of astronomy is divided according to their duties and fields of interest. Research systems are divided into categories within themselves for reasons such as research methods and tools. The sub-branches of astronomy are listed as follows according to their subjects.
1) Archeoastronomy
It is a sub-branch of astronomy that examines how the events in the sky were recorded by humans when they first started to examine how they set up systems. It examines how and why the systems they set up and how these systems cause changes in the cultural and social life of that society.
It examines the interpretation and interpretation of celestial events by ancient civilizations. Archeoastronomy; They are related to many fields of science such as archeology, ethnography, mythology and anthropology and they benefit from each other.
2) Astrophysics
Another sub-branch of astronomy is astrophysics. Astrophysics is also called astrophysics or stellar physics. Astrophysics is a sub-branch of astronomy that uses the laws of physics and chemistry to apply them to celestial bodies and all objects in the universe, to explain their birth, phases and death. Astrophysics seeks to find and understand the universe and our place in it.
Examines and interprets the light and electromagnetic waves emitted from celestial bodies. In fact, it is a combination of physics and astronomy sciences. Because of the universality of the laws of physics and chemistry, they can apply it to the entire universe, to the star system. It is an interdisciplinary science, and not only astronomy and physical sciences, but also branches of science such as mathematics, geology and chemistry are used.
3) Astrobiology
In other words, exobiology is another sub-branch of astronomy. The emergence of life in the universe and the biological properties of life forms that may exist in the objects in the sky, their distribution and the future of these forms. It explores the possibility of life appearing on other planets or celestial bodies, inside or outside the Solar System, as it did on earth.
Astrobiology, one of the sub-branches of astronomy, also benefits from sciences such as chemistry, physics and ecology. It also deals with extraterrestrial life. He also conducts research on the first existence of life, that is, early life forms, and compares his theoretical knowledge with other celestial bodies.
4) Astrogeology
Planetary earth science or astrogeology. Astrogeology, one of the sub-branches of astronomy, is a science that studies the geology of planets, moons, asteroids, comets and meteorites. It is the science that studies the formation and development of celestial bodies in terms of their structures. It is a branch of science that studies the outer layer, namely the earth’s crust, of large and small meteorites, planets and moons.
5) Astrochemistry
It is one of the sub-branches of astronomy that studies chemical elements and substances found outside our world. It studies and studies the interactions of these elements and substances with each other and the molecular gas clouds larger than the Solar System. It measures the composition and temperatures of objects far from Earth using telescopes of different sizes.
6) Galactic Astronomy
Galactic astronomy, also called galactic science, is the science that deals with our Milky Way galaxy, that is, everything that happens at the borders of our galaxy.
7) Extragalactic Astronomy
Extragalactic astronomy is one of the sub-branches of astronomy that studies objects outside the Milky Way galaxy. It can be thought of as the next level of galactic astronomy. He studies galaxy clusters and groups, intergalactic dust clumps, supernovae.
8) Physical Cosmology
Physical cosmology, or physical cosmology, is one of the sub-branches of astronomy. It deals with the structures in the universe and the development of the universe. It deals with issues related to how the universe was formed and the evolution process. Physical cosmology began with Albert Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity and evolved through better observation of objects far from Earth. Physical cosmology made predictions about the formation of the universe and allowed scientists to produce the Big Bang theory.
9) Celestial Mechanics
It is a branch of astronomy that studies the movements of celestial bodies. The relationships determined by the gravitational interactions of celestial bodies are based on Kepler’s mathematical model. It is based on the theory of applying the laws of physics, which was later developed by Newton and formed the basic laws of motion. However, according to Einstein’s General Theory of Relativity, it has been revised and some problems that have arisen with more precise measurement methods have been solved.
10) Radio Astronomy
It is a branch of astronomy that studies electromagnetic radiation in the field of radioelectric waves of celestial bodies. Karl G. Jansky discovered in 1931 that objects radiate with radio waves. It produces electromagnetic energy due to the fact that the objects have a temperature above absolute zero. The frequency distribution in the universe changes depending on the temperature. According to the theory, electromagnetic energy emanating from all objects in the universe can be measured.
11) X-Ray Astronomy
X-ray astronomy is a branch of astronomy that deals with the study of the observation and detection of X-rays of astronomical objects. It is an astronomy science concerned with space telescopes that see farther than telescopes with light absorption. The energy required for X-ray absorption is produced by gravity.
12) Ultraviolet Astronomy
Ultraviolet astronomy, or ultraviolet astronomy, is the observation of electromagnetic radio at wavelengths of ultraviolet light between about 10 and 320 nanometers, and the short wavelengths, high energy photons, gamma-ray astronomy are investigated. Ultraviolet rays are invisible to the naked eye, and our atmosphere absorbs most of the light of this wavelength. For this reason, observations must be made from above the atmosphere or from space.
13) Observational Astronomy
Observational astronomy, different from astronomy and astrophysics, is a branch that deals with data acquisition. It aims to observe celestial bodies using telescopes and other astronomical instruments, that is, to find measurable properties of physical models. The most suitable place for optical telescopes established for observation purposes is space.
The reason is that observational astronomy, which is a sub-branch of this astronomy, can make better observations without being affected by atmospheric events. Because of this expensive method, the most suitable areas are the mountain peaks. The increase in artificial lights, that is, the increase in urbanization, negatively affects this branch of science due to background light emission, and therefore special filters are used.
14) Astrometry
Astrometry, also known as astrometry, is the science of astronomy that allows the positions, movements and positions of stars and other celestial bodies to be measured with high precision. Astronomers constantly monitor changes in the positions of objects. These measurements are based on star catalogs.
These catalogs give reference points for celestial bodies and astronomers keep track of these reference points. These catalogs are It goes back to Hipparkos, who lived in 190 BC. In 1989, celestial measurement was carried into Earth orbit with the Hipparchus satellite.
The star catalog used today is known as USNO-B1.0. The movements, positions, angular changes and characteristic features of more than 1 billion celestial bodies are recorded.