Do you know how and when the first heart transplant took place? Approximately 4,000 heart transplants are performed around the world each year. So what is the history of heart transplantation, which is so vital, and how has it progressed?
The first known heart transplant in history
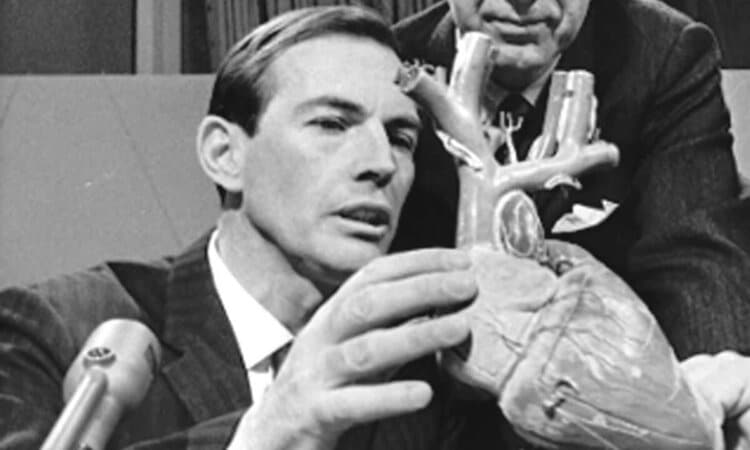
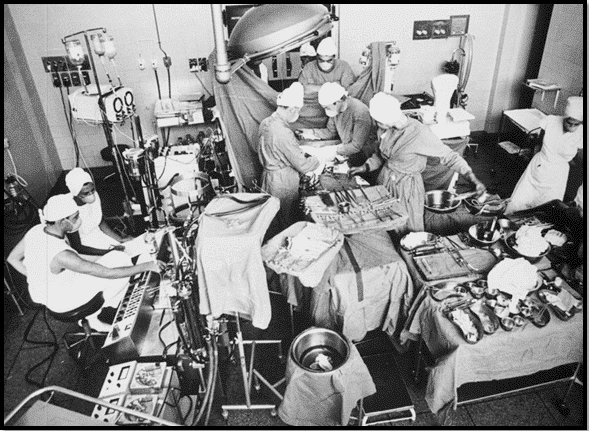
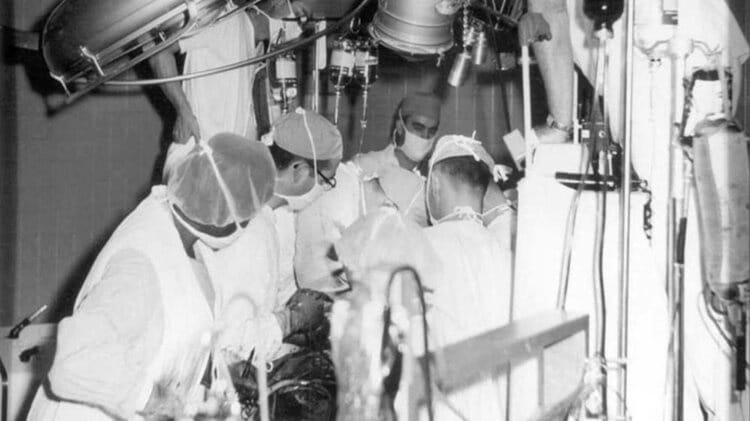
Successful scientist, physician, who performed the first human-to-human heart transplant surgery, as well as human-to-human. It is Christiaan Barnard. We will tell about the heart transplant that took place in 1967 and shook the world, and the scientific events that took place until this time. Heart transplantation is the replacement of a sick heart with a healthy human heart, which can no longer fully fulfill or completely lose the functions of a healthy heart.
It is the transplantation of organs taken from people who donate organs, which are also called donors in scientific language, to people in emergency situations. Heart transplant surgery is perhaps a miraculous event for us people, who save the lives of many people and offer them a new life. Of course, the heroes who donated their organs for the realization of this surgery should not be forgotten.
Well, what kind of scientific developments have taken place in the period until the first heart surgery?
17th date of organ transplant. We can take it to the century. For example, the first skin transplant surgeries were tried. In 1863, Paul Bert experimented with non-vascular transplantations in male ovaries and teeth and wrote about tissue incompatibilities. In 1883, transplant attempts were made on damaged internal organs.
Organ transplant trials in the 20th century
At the beginning of the twentieth century, in 1902, Emerich Ullmann and Alexis Carrel wanted to perform a transplant (organ transplant) on two dogs and relocated the dogs’ organs. Alexis Carell noticed tissue incompatibility in organ transplants between two people. Carell also developed techniques for cutting and suturing veins. Thanks to these techniques he developed, he won the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1912.
First human transplant trials
The first organ transplant surgery trial on humans was made by the Frenchman Mathieu Jaboulay in 1916. This surgery was unsuccessful because animal organs were used. He was unsuccessful as he tried to transplant pig and sheep kidneys to two women whose kidneys were no longer functioning and were dying. In 1908, a dog’s own organs were transplanted and the dog lived for a long time since there was no organ incompatibility. In 1909 in Germany, Dr. Unger tried to connect a monkey kidney to a girl with a vein on her thighbone, but failed.
Reasons for failed transplant attempts
The reason why many organ transplant attempts fail in many countries is because there is no solution to the body’s resistance problem. Almost all transplants resulted in death. British zoologist Peter Brian Medawar, who found that the body’s resistance was related to the immune system, received the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1960. In order to prevent the immune system’s reactions, patients were given radiation therapy, and because these rays were so harmful, patients were dying.
Successful first organ transplant
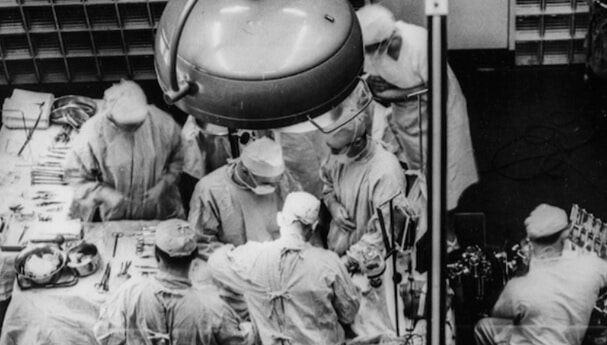
The first successful organ transplant was performed by Joseph Murray in 1954. The donor patient was an identical twin and immune-related reactions were minimized. The transplant patient lived for eight years and died of a heart attack. Murray received the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1990. There were also trials in 1951 and 1952, but the patients lived and died for a short time. The first successful human-to-human lung transplant was performed by James Hardy.
First animal-to-human heart transplant surgery
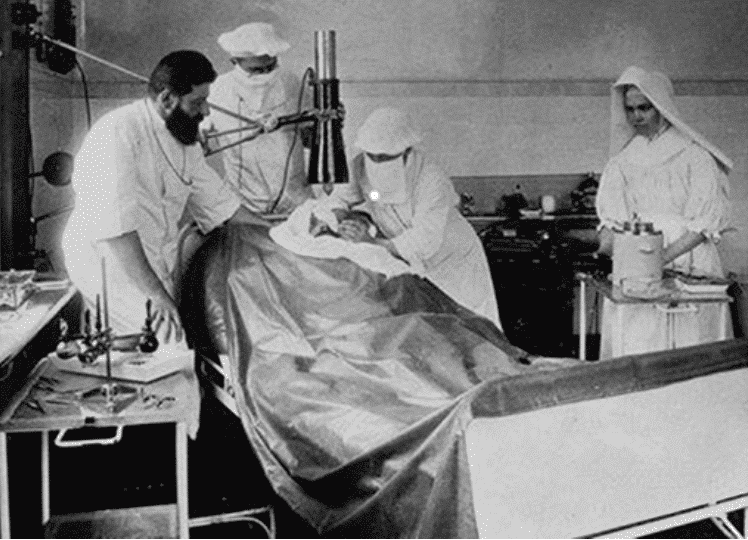
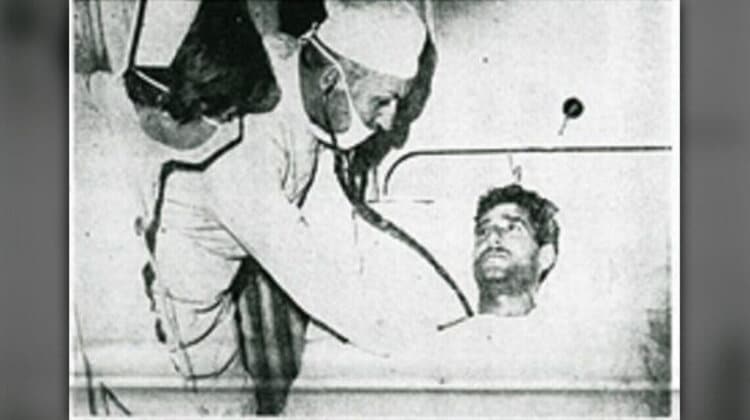
He transplants the heart taken from a chimpanzee by James D. Hardy at the University of Mississippi in 1964 to Boyd Rush, a 68-year-old comatose patient whose heart is about to stop. Hardy, who could not find a human donor heart, used a chimpanzee heart. The heart, which works for about an hour, is rejected by the body. After this surgery, hearts taken from animals such as sheep, pigs and monkeys were tried to be transplanted into humans. His use of the chimpanzee heart later led to some controversy.
The first human-to-human heart transplant, Dr. Who is Christian Barnard?
Barnard, who opened his eyes in Beaufort West city of Cape Province of South Africa in 1922, performed this important organ transplant that changed the course of the history of science. Barnard graduated from medical school in the same city in 1951 and started working in hospitals. He did his doctoral studies at the University of Minnesota and proved that the reason for the congenital obstruction of the small intestine is due to the insufficient blood supply to the fetus during pregnancy. He received the title of professor of surgery in 1972. He passed away in 2001.
Dr. Christiaan Barnard transplant trials
Dr. Christiaan Barnard tried to perform several organ transplant trials using dogs and chimpanzees in South Africa. In 1974, it became a pioneer again by making a new attempt by adding a second heart to support the work of the heart without removing the unhealthy heart of a patient for the first time.
First heart transplant ‘human-to-human’
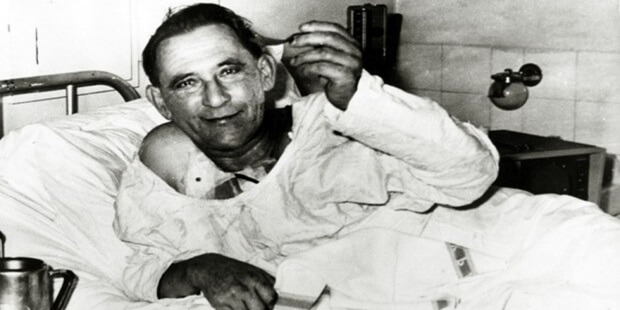
In 1967, Dr. Christiaan Barnard performed the first heart transplant surgery for her patient named Louis Waskansky, which will resonate with the whole world and will be talked about a lot. Dr. In this surgery performed by Christiaan Barnard, his patient, Louis Waskansky, survived for 18 days and died due to infection. Dr. Christiaan Barnard transplanted a heart from a brain-dead vegetative patient to her patient. He wrote his name in the history of science with the first heart transplant surgery.
First heart transplant surgery and after
The first human-to-human heart transplant was successfully performed, but the body’s immune system began to react. The patient Louis Waskansky was weakened so that the transplanted heart would not resist its proteins. But because he was debilitated, he contracted pneumonia and only lived for 18 days and died.
Dr. Christiaan Barnard’s second alpine transplant attempt
Dr. Christiaan Barnard tried the second surgery after her first heart transplant surgery. In this heart transplant surgery trial, the patient died after surviving more than a year. Most of the heart transplants that were performed later failed because the problems of foreign tissue and organ rejection by the body’s immune system could not be resolved.
First organ transplant in Turkey
On November 3, 1975, Prof. Dr. The first organ transplant was performed by Mehmet Haberal at Hacettepe University. It was carried out with an organ transplant from a mother to her son. For this reason, events are organized as Organ Transplant Week between 3-9 November.
In 1979, Prof. Dr. Mehmet Haberal and his team performed the first kidney transplant surgery from a local cadaver by taking the kidney from a person who died in a traffic accident. On December 8, 1988, Prof. Dr. Mehmet Haberal performed Turkey’s first liver transplant operation. prof. Dr. Mehmet Haberal and his team performed 1507 kidney and 122 liver patients’ surgeries.
First heart transplant surgery in Turkey
In 1966, Dr. He performed Christiaan Barnard’s human-to-human heart transplant surgery. After this surgery, Op. Dr. Kemal Bayazıt performed the first heart transplant operation on a patient with severe heart failure named Maviş Karagöz in Ankara Yüksek İhtisas Hospital in 1968.
Surgery was to be performed with a heart taken from a young woman who had been brain dead in a traffic accident. The operation, which started at three o’clock at night, finished at six o’clock in the morning. This first heart transplant was successfully completed, but the patient died as a result of bleeding that started a few hours later. Two days after this heart transplant, Prof. Dr. Siyami Ersek, although the operation was successful, the patient died a few days later.