Fibrous foods are very important for your nutrition and health. Unlike most other foods, they leave your stomach undigested and reach your intestines. In your gut, it nourishes the intestinal flora , helps bacteria, and plays a role in many different beneficial and healthy functions.
Some fibrous foods also support weight loss, lower your blood sugar levels and are great helpers in the fight against constipation.
Nutritional authorities recommend consuming an average of 14 grams of fiber for every 1,000 calories you consume daily. This amount corresponds to an average of 24 grams of fiber per day for women and 38 grams for men.
Unfortunately, according to research by the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, an estimated 95% of American adults and children do not meet the recommended daily fiber intake. The average daily fiber intake in the United States is estimated to be 16.2 grams.
Increasing your fiber intake is relatively easy – just include high-fiber foods in your diet and you’ll quickly see the benefits.
What Is Fiber Found in Fibrous Foods?
Fiber is a generic term for any type of carbohydrate your body can’t digest. The fact that your body doesn’t use fiber as fuel doesn’t make it any less valuable to your overall health.
The term “dietary fiber” refers to the indigestible parts of plant-based foods. In other contexts, “fiber” may refer to plant-based fabric, but the terms “fiber” and “dietary fiber” are often used interchangeably when talking about nutrition.
Fiber is important for digestion and toilet regularity, weight management, blood sugar regulation, cholesterol maintenance and more. It is also linked to longevity and reduced cancer risk.
According to Colorado State University, fiber falls into two categories: soluble and insoluble fiber.
Simply put, while soluble fibers such as pectin, gum, and mucilage dissolve in water; Insoluble fibers such as hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignin do not show the same response. As soluble fiber is digested in the body, it dissolves and becomes a gel-like substance. Insoluble fiber mostly retains its shape while in the body.
Both soluble and insoluble fiber have significant benefits. Soluble fiber is known to help lower blood sugar levels. It also helps lower blood cholesterol.
Insoluble fiber speeds up the passage of food through the digestive system. This helps prevent constipation in general. It also increases stool volume, which makes it easier for stools to pass.
Most plant-based foods contain both soluble and insoluble fiber, but the amount of each varies in different foods. Good sources of soluble fiber include beans, lentils, oatmeal, peas, citrus fruits, blueberries, apples and barley. Good sources of insoluble fiber include foods that include whole wheat flour, wheat bran, brown rice, cauliflower, potatoes, tomatoes, and cucumbers. Some foods, such as nuts and carrots, are good sources of both types of fiber.
What Are Fibrous Foods Beneficial?
Fibrous foods aid digestion
Dietary fiber helps improve digestion by increasing stool volume and regularity. This is probably the most well-known benefit of fiber foods. Larger, softer stools are healthier and easier to remove than hard or watery stools, which not only makes life more comfortable, but also helps maintain colorectal health. A high-fiber diet helps reduce the risk of hemorrhoids and diverticulitis (small, painful pouches in the colon). Fibrous foods are used as a solution to many stomach problems.
Fibrous foods are good for heart health
Fiber also helps lower cholesterol. The digestive process requires bile acids, which are partly formed by cholesterol. As your digestion improves, the liver pulls cholesterol from the blood to create more bile acids, thereby reducing the amount of LDL (bad) cholesterol.
promoting blood sugar control
It takes longer for your body to break down high-fiber foods. Foods high in fiber help you maintain more consistent blood sugar levels, which is especially beneficial for people with diabetes.
Fibrous foods fight possible cancer
While the National Cancer Institute claims that a high-fiber diet does not reduce risk to a clinically significant degree, a 2011 meta-analysis from the British Journal of Medicine found a negative association between cereal fiber and colorectal cancer risk.
A more recent animal experiment has suggested that fiber can cause this benefit only if a person has the right type and amount of gut bacteria. Fiber naturally reacts with bacteria in the lower colon and can sometimes ferment into a chemical called butyrate, which can cause cancer cells to self-destruct. Some people naturally have more butyrate-producing bacteria than others, and a high-fiber diet can help encourage the growth of bacteria.
Eating enough fiber may have protective effects against certain types of cancer, including colon cancer. There are many reasons for this, including the fact that some types of fiber, such as pectin in apples, have antioxidant-like properties.
Long life
A recent study suggests that grain fiber from foods such as whole-grain bread, cereal, and pasta is particularly effective. Over a 14-year period, those who ate the most grain fiber were 19 percent less likely to die than those who ate the least. This proves its usefulness in the name of fibrous foods.
New research suggests that fiber may play a role in preventing food allergies, the existence of which has long puzzled scientists. Again, this theory comes down to the interaction between fiber and bacteria in the gut.
Allergic reactions and asthma
Scientists theorize that people are not producing the right gut bacteria to combat allergens from foods commonly associated with allergies, such as peanuts and shellfish. Without the right bacteria, particles of these foods enter the bloodstream through the gut. Fiber helps produce a bacteria called Clostridia, which helps keep the gut safe.
The same logic explains why fiber can help people with asthma. Unwanted particles that escape from the intestinal flora and enter the bloodstream can cause an autoimmune response such as asthma. A 2013 animal experiment found that mice fed a high-fiber diet were less likely to experience asthma inflammation than mice fed a low- or moderate-fiber diet.
Fiber provides many health benefits, but it’s important to gradually introduce fiber-containing foods into your diet over a few days to avoid negative effects like bloating and gas.
What are fiber foods?
Pears: Medium, 5.5 grams per fresh pear or 3.1 grams per 100 grams
Strawberries: There are 2 grams of fiber in 100 grams of strawberries.
Avocado: 10 grams per 1 cup of fresh avocado or 6.7 grams per 100 grams
Apple: Medium, 4.4 grams per fresh apple or 2.4 grams per 100 grams.
Raspberries: One cup of fresh raspberries contains 8 grams of fiber, or 6.5 grams of fiber per 100 grams.
Banana: A medium banana contains 3.1 grams of fiber. There are 2.6 grams of fiber per 100 grams.

Other high fiber fruits
Blueberries: 2.4 grams per 100 gram serving.
Blackberries: 5.3 grams per 100 gram serving.
Carrots: 100 grams of fresh carrots contain 2.8 grams of fiber.
Beets: 100 grams of fresh beets contain 2.8 grams of fiber.
Broccoli: 2.6 grams of fiber per 100 grams.
Artichokes: 6.9 grams per spherical artichoke or 5.4 grams per 100 grams.
Brussels sprouts: 3.7 grams per 100 grams of raw Brussels sprouts.
Other high fiber vegetables
Spinach: 2.2 grams per 100 grams of spinach.
Tomatoes: 1.2 grams per 100 grams of tomatoes.
Lentils: 7.3 grams per 100 grams of cooked lentils.
Kidney beans: 6.8 grams per 100 grams of cooked kidney beans.
Peas, peeled: 8.3 grams per 100 grams of cooked peas.
Chickpeas: 7.6 grams of fiber in 100 grams of cooked chickpeas.
Other high fiber foods:

Cooked black beans: 8.7 grams per 100 grams.
Cooked edamame: 5.2 grams per 100 grams.
Cooked lima beans: 7 grams per 100 grams.
Dry beans : 5.5 grams per 100 grams.
Oats: 10.1 grams of fiber per 100 grams of oats.
Popcorn: 14.4 grams per 100 grams.
Other high fiber grains
Almonds: 13.3 grams of fiber in 100 grams of almonds.
Chia seeds: 34.4 grams per 100 grams
Fresh Coconut: 9 grams
Pistachios: 10 grams
Walnuts: 6.7 grams
Sunflower seeds: 11.1 grams
Pumpkin seeds: 6.5 grams
Sweet potato: A medium boiled sweet potato contains 3.8 grams of fiber, while 100 grams of sweet potatoes contain 2.5 grams of fiber.
All values are for 100 gram portion.
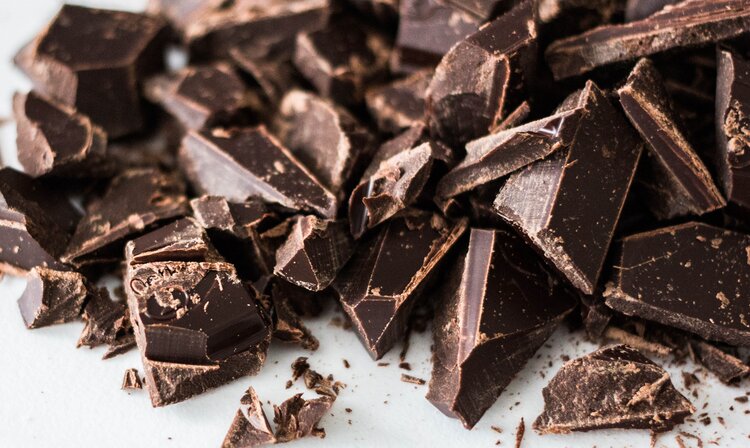
Dark chocolate
Dark chocolate is arguably one of the world’s most delicious and at the same time beneficial fiber foods. Be sure to choose only dark chocolate with a cocoa content of 70-95% or higher, and avoid products with added sugar.
Fiber content: 10.9 grams per 100 grams